Follow us and share.
Do You Have Mice in Your Home? Learn the Risks of Hantavirus and How to Avoid Them
Living in close quarters with rodents, especially in rural areas or under unhygienic conditions, poses a significant risk to human health. Among the most dangerous diseases they can transmit is hantavirus, a potentially fatal infection that affects the respiratory system.
Learn about the risks of hantavirus and other mouse-borne diseases. Learn how they spread, what symptoms they cause, and how to prevent them from spreading in your home.

Living in close quarters with rodents, especially in rural areas or under unhygienic conditions, poses a significant risk to human health. Among the most dangerous diseases that can be transmitted is hantavirus, a potentially fatal infection that affects the respiratory system. In this article, you'll learn what hantavirus is, how it's transmitted, what other diseases mice can transmit, and how to effectively prevent them.
This content is optimized to help you prevent rodent-borne diseases, detect early symptoms, and adopt effective home control strategies. If you're looking for ways to prevent hantavirus, how to get rid of mice, or what diseases rodents cause, you'll find clear and up-to-date answers here.
📌 What is hantavirus and how is it transmitted?
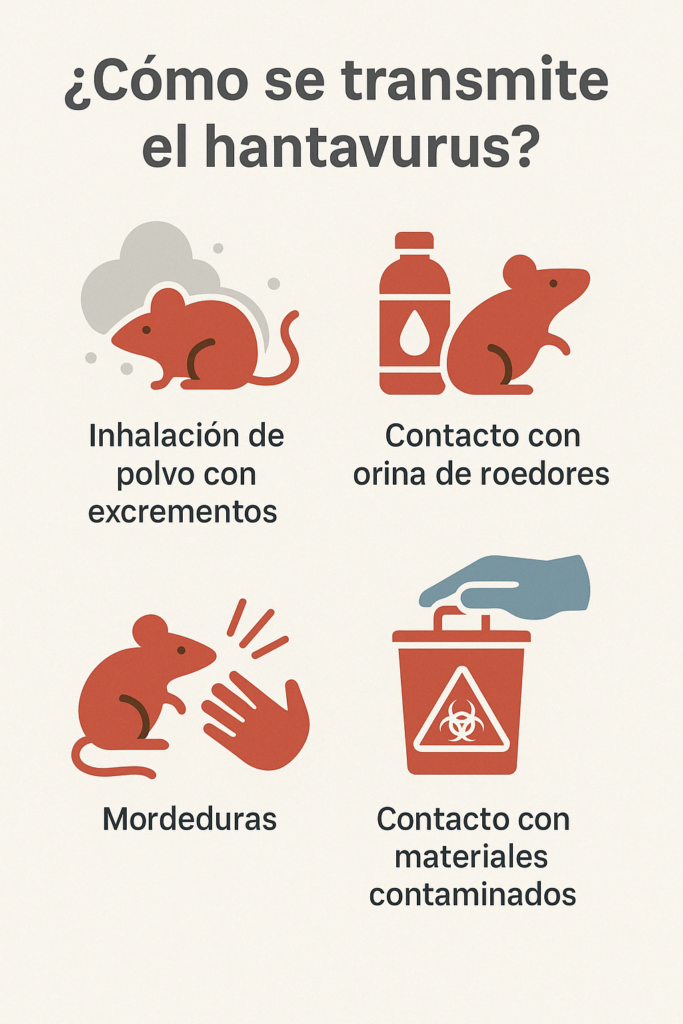
He hantavirus It is a virus transmitted by wild rodents, particularly field mice of the genus OligoryzomysPeople can become infected primarily by:
- Inhaling viral particles present in dust contaminated with mouse urine, feces, or saliva.
- Having direct contact with rodent droppings.
- Receiving bites from infected mice.
- Handling contaminated materials without adequate protection.
Once contracted, the infection can trigger the hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS), characterized by fever, muscle aches, respiratory distress and, in severe cases, respiratory failure that may require admission to intensive care.
The incubation period is usually one to five weeks after contact with the virus. It progresses rapidly and requires urgent medical attention. The mortality rate can exceed 35% if not detected early.
📌 Other diseases transmitted by mice
In addition to hantavirus, rodents can be vectors of other infectious diseases such as:
- Leptospirosis: Caused by bacteria present in mouse urine. It is transmitted through contact with contaminated water or soil. It can affect the liver and kidneys and cause high fever, jaundice, muscle aches, and even multiple organ failure.
- Salmonellosis: A bacterial infection acquired by consuming food or water contaminated with rodent feces. It causes diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, and vomiting. It is especially dangerous for young children and immunocompromised individuals.
- Rat bite fever: Transmitted by bacteria present in rodent saliva. It occurs after bites or scratches and can cause persistent fever, rash, and severe joint pain.
- Bubonic plague: Although very rare today, plague is still present in endemic regions and can be transmitted by infected fleas that parasitize mice. Its symptoms include high fever, swollen glands, and general weakness.
Rodents can also cause respiratory allergies or asthma by releasing allergens in their droppings and urine, which contaminate the air indoors.
📌 Risks of living with mice
Having mice in your home or surrounding area poses a direct health risk. Their presence can:
- Contaminate food, utensils and surfaces with their excretions.
- Trigger serious infectious diseases through direct or indirect contact.
- Damage to structures, wiring, and building materials, increasing the risk of fires or short circuits.
- Creating unhealthy environments, especially dangerous for children, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems.
- Alter psychological well-being, causing anxiety or insomnia when sensing the presence of pests in the home.
The symptoms of these illnesses can be confused with those of the flu or common respiratory illnesses, delaying diagnosis and treatment and increasing the risk of complications.
📌 Prevention and control measures
The best way to protect yourself is to keep rodents out of your environment. Some key preventative measures include:
- Maintain cleanliness of your home, warehouses, and cellars, avoiding the accumulation of waste, papers, or unused materials.
- Seal cracks, crevices, drains, and potential entrances to the home with metal mesh or silicone.
- Store food in airtight containers and keep it out of reach of pests.
- Remove accumulations of trash, firewood, or debris near the home that serve as shelter for rodents.
- Ventilate closed spaces for at least 30 minutes before entering if infestation is suspected.
- Clean potentially contaminated areas with gloves and a mask, spraying them with disinfectant solution beforehand to avoid raising dust.
- Consult with pest control professionals for severe or persistent infestations.
If you live in rural areas or engage in outdoor activities (such as camping, working in fields or sheds), it's important to take extra precautions: avoid sleeping directly on the ground, drink safe drinking water, and avoid handling dirty objects without protection.
💡 Final Reflection: Living with rodents is a risk that can be avoided.
Mice are not just a nuisance; they pose a real risk to public health. Prevention begins at home, with hygiene habits, proper storage, and environmental control. Acting in time can save lives.
Don't wait to detect symptoms to take action. Protecting your home from rodents and maintaining good environmental hygiene is essential to prevent outbreaks of dangerous diseases such as hantavirus, leptospirosis, and salmonellosis.
This content is optimized with strategies SEO and SEM to help you identify the risks of hantavirus, know how eliminate mice from the home and implement effective measures prevention of rodent-borne diseases.



