Follow us and share.
Myocardial Infarction: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Myocardial infarction: Learn its causes, symptoms, and how to prevent it. Learn to identify warning signs and what to do in an emergency. Protect your cardiovascular health.
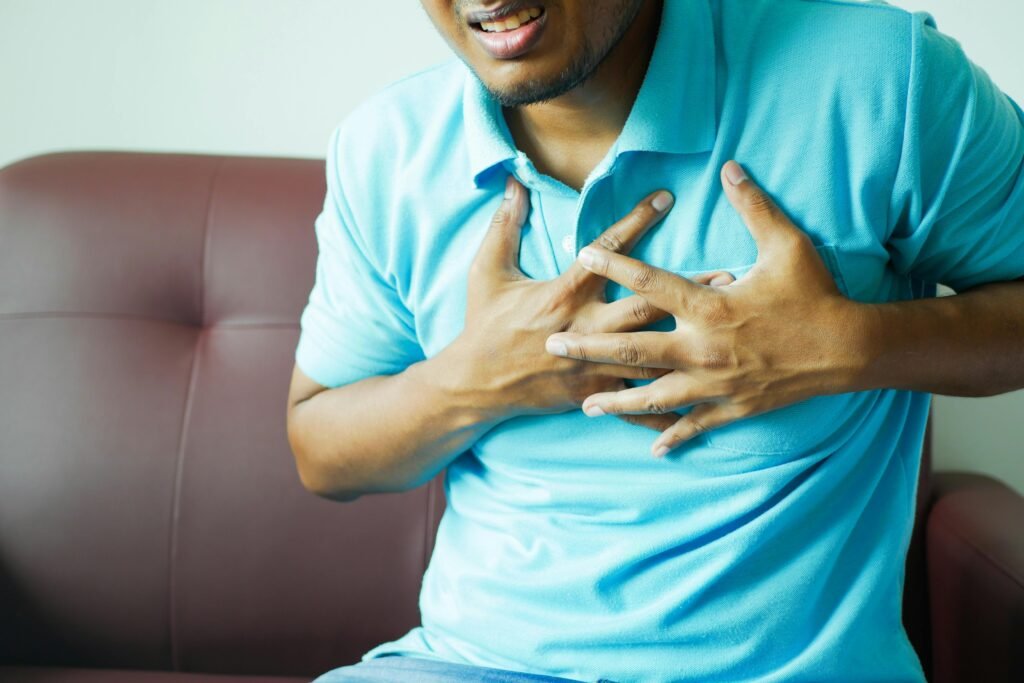

He myocardial infarction, also known as heart attack, is a serious condition that occurs when blood flow to a part of the cardiac muscle appears blocked. This obstruction is usually caused by the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques or the formation of blood clots in the coronary arteries. When oxygen does not reach the heart properly, heart cells begin to die, which can cause irreversible damage and put the patient's life at risk.
This event is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. The faster you act, the greater the chances of recovery and the fewer the complications.
Main Causes of Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial infarction is usually the result of a blockage in the coronary arteries, which prevents proper blood flow to the heart. The main causes include:
- Atherosclerosis: It involves the accumulation of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in the arteries, forming plaques that reduce or block blood flow.
- Blood clots: They can form on atherosclerotic plaques, completely impeding circulation.
- Arterial spasms: A sudden narrowing of the coronary arteries, due to factors such as stress, drug use, or smoking, can disrupt the oxygen supply to the heart.
- Risk factors: High blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and smoking are conditions that significantly increase the likelihood of suffering a heart attack. American Heart Association – Information on heart disease prevention.
Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction
Identifying the symptoms of a heart attack early can mean the difference between life and death. Some of the most common signs include:
- Chest pain: It can present as intense pressure or a tight feeling in the center of the chest. In many cases, this pain can radiate to the left arm, jaw, neck, or back.
- Difficulty breathing: Feeling short of breath, even without physical exertion.
- Nausea and excessive sweating: It may be accompanied by vomiting in some cases.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: Feeling weak or faint, which may indicate a drop in oxygen supply to the brain. Mayo Clinic – Symptoms and diagnosis of myocardial infarction.
Prevention of Myocardial Infarction
While some risk factors, such as family history, cannot be modified, there are several strategies to significantly reduce the likelihood of having a heart attack:
- Maintain a healthy diet:
- Reduce your consumption of saturated and trans fats.
- Increase your intake of fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich foods.
- Consume omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, nuts and seeds.
- Perform physical activity regularly:
- It is recommended at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week.
- Walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent options for strengthening your heart.
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol:
- Have regular checkups with your doctor.
- If you suffer from hypertension or high cholesterol, follow the recommended treatment.
- Quit smoking and reduce alcohol consumption:
- Smoking damages the arteries and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and contribute to obesity.
- Managing stress effectively:
- Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation and deep breathing can help reduce stress.
- WHO – WHO recommendations on the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
What to Do in Case of a Myocardial Infarction?
If you suspect someone is having a heart attack, it is crucial to act immediately. Follow these steps:
- Call emergency services immediately (911 or other local number).
- Stay calm and help the person sit or lie down.
- If the person is conscious and not allergic, give them an aspirin. This may help reduce the formation of clots.
- If the person loses consciousness and is not breathing, begin Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) until emergency services arrive.
Importance of Prevention and Rapid Action
Myocardial infarction is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, but with a preventative approach and immediate care, many lives can be saved. Adopting healthy habits, getting regular medical checkups, and knowing the symptoms can make a difference. If you experience any warning signs, act immediately and seek medical help.