Follow us and share.
Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: Differences, Causes, and Warning Signs
The cerebrovascular accidents (CVA) are medical emergencies that can leave permanent after-effects or even cause death if not treated promptly. There are two main types: Ischemic stroke and the Hemorrhagic stroke, and although the symptoms may be similar, their causes, treatments and prognoses are very different.
📌 In this guide we explain in a simple way what the Differences between an ischemic and a hemorrhagic stroke, what causes them, what their warning signs are, and how to prevent them.
📌 What is a stroke?
A stroke, also called stroke, occurs when a part of the brain stops receiving oxygen-rich blood. This causes the affected neurons to die, rendering them unable to regenerate, which can affect vital functions such as speech, movement, or memory.
In the medical field it is also called cerebral vascular event (CVE) either cerebral infarction, depending on its nature.
📌 What is an ischemic stroke?
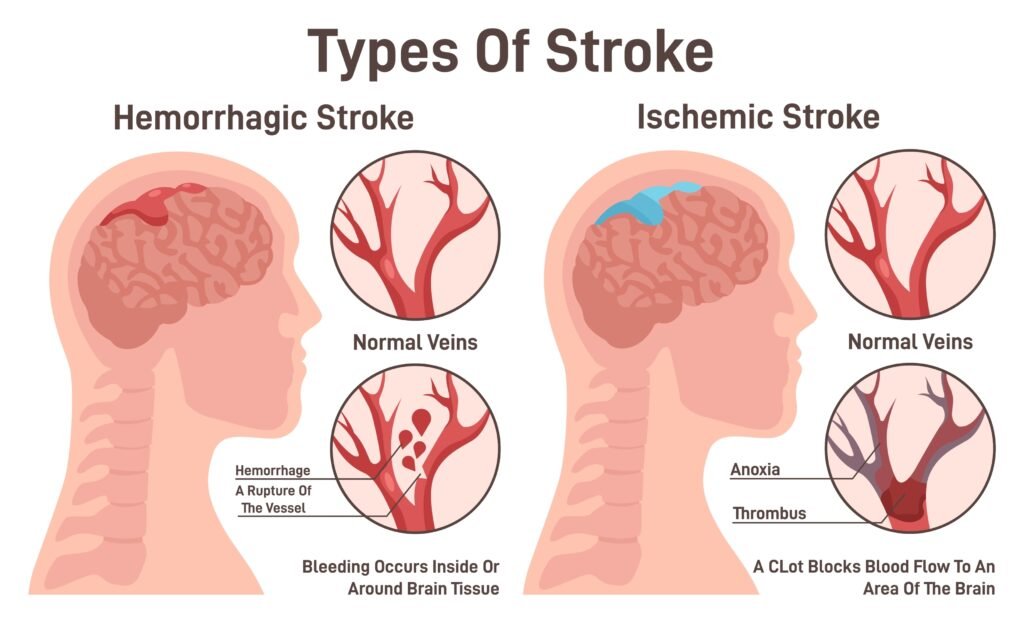
He Ischemic stroke It is the most common type of stroke, accounting for nearly 85% of the cases. It occurs when an artery that carries blood to the brain is blocked. blocked by a clot, preventing the passage of oxygen to brain tissue.
👉 And what is cerebral thromboembolism?
He cerebral thromboembolism It is one of the main causes of ischemic stroke. It occurs when a thrombus (blood clot) in another part of the body—usually the heart or arteries in the neck—and travels to the brain, blocking a brain artery. This is called cerebral embolism.
This type of event is considered a acute cerebral ischemia and requires immediate attention. According to the Mayo Clinic, most ischemic strokes are caused by atherosclerosis (accumulation of fat in the arteries) or by atrial fibrillation, a cardiac arrhythmia that promotes the formation of clots.
📌 What is a hemorrhagic stroke?
He Hemorrhagic stroke accounts for the remaining 15% cases, but its lethality is higher. It occurs when a blood vessel ruptures inside the brain, causing bleeding that damages brain tissue.
Among its most common causes are:
- Untreated chronic high blood pressure
- Brain aneurysms
- Head injuries or head trauma
- Coagulation disorders or use of anticoagulants
Unlike ischemic stroke, which requires clot-dissolving drugs, Hemorrhagic stroke requires stabilizing the patient, control blood pressure and, in many cases, surgery to stop the bleeding.
| Feature | Ischemic stroke | Hemorrhagic stroke |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Obstruction by clot or embolism | Rupture of a blood vessel |
| Frequency | Very common (85% cases) | Less common (15%) |
| Onset of symptoms | It can be progressive or sudden | Sudden, with severe symptoms |
| Headache | Infrequent | Intense and sudden |
| Initial treatment | Anticoagulants, thrombolytics | Blood pressure control and surgery |
| Forecast | It is better to act in time | High risk of death or sequelae |
Understanding this difference is critical, as treatment will depend on the type of stroke and the timing of medical care.
📌 Warning signs of a stroke
Acting quickly is key. Some symptoms may indicate that someone is suffering from a cerebrovascular event, whether ischemic or hemorrhagic:
✅ Sudden weakness in the face, arm, or leg (especially on one side of the body)
✅ Difficulty speaking or understanding
✅ Visual problems in one or both eyes
✅ Dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
✅ Sudden, severe headache (more common in hemorrhagic stroke)
🧠 As explained by the CDC, use the acronym FAST can help you remember the basic steps to detect a stroke:
- Face: Is the face drooping on one side?
- TOrms: Can you raise both arms?
- Speech: Is speech slurred or incoherent?
- Ttime: Call emergency services immediately.
📌 Stroke diagnosis and treatment
To confirm whether it is an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, doctors often use tests such as:
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Cerebral angiography
In case of ischemic stroke:
- It can be administered thrombolytics, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), if the patient arrives within the first 3 to 4.5 hours.
- In some cases, a mechanical thrombectomy to remove the clot.
In case of hemorrhagic stroke:
- The patient is stabilized by controlling blood pressure.
- The effect of anticoagulants can be discontinued or reversed.
- In severe cases, it is performed surgery to drain blood or repair the broken glass.
The choice of appropriate treatment depends on an accurate and rapid diagnosis.
📌 Prevention: Can a stroke be avoided?
The good news is that More than 80% of strokes can be prevented, according to data from the American Stroke Association.
Here are some essential recommendations:
✔️ Keep your blood pressure under control
✔️ Exercise regularly
✔️ Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
✔️ Follow a healthy diet, low in fat and salt
✔️ Controls diseases such as diabetes and high cholesterol
✔️ Consult your doctor if you have arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, to prevent the formation of clots
Also, if you have already had a stroke or are at high risk, you will probably need to take medications such as aspirin either anticoagulants to prevent further events.
💡Make decisions now to protect your brain tomorrow
Both the Ischemic stroke like the hemorrhagic They can change your life in seconds. But with information, prevention, and a quick response, they can also be prevented or their impact reduced.
Knowing the warning signs, acting quickly, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are your best bets to avoid complications. Share this information, it could save a life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is cerebral thromboembolism the same as an ischemic stroke?
Not exactly. It's one of the main causes of ischemic stroke, but not all cases involve it. A thromboembolism occurs when a clot travels and blocks an artery in the brain.
2. How do you distinguish a hemorrhagic stroke from an ischemic stroke?
Imaging studies only. Although hemorrhagic stroke often presents with severe headache, it's not possible to distinguish them with certainty without a CT scan or MRI.
3. How quickly should I act on symptoms?
Immediately. The sooner the patient arrives at the hospital, the greater the chances of recovery, especially in ischemic stroke.
4. Is a stroke reversible?
Some patients recover completely, especially if they receive medical care within the therapeutic window. Others may be left with permanent after-effects.
5. Can you live a normal life after a stroke?
Yes, many people do. However, it depends on the type of stroke, the severity of the damage, and access to physical, speech, or cognitive rehabilitation.